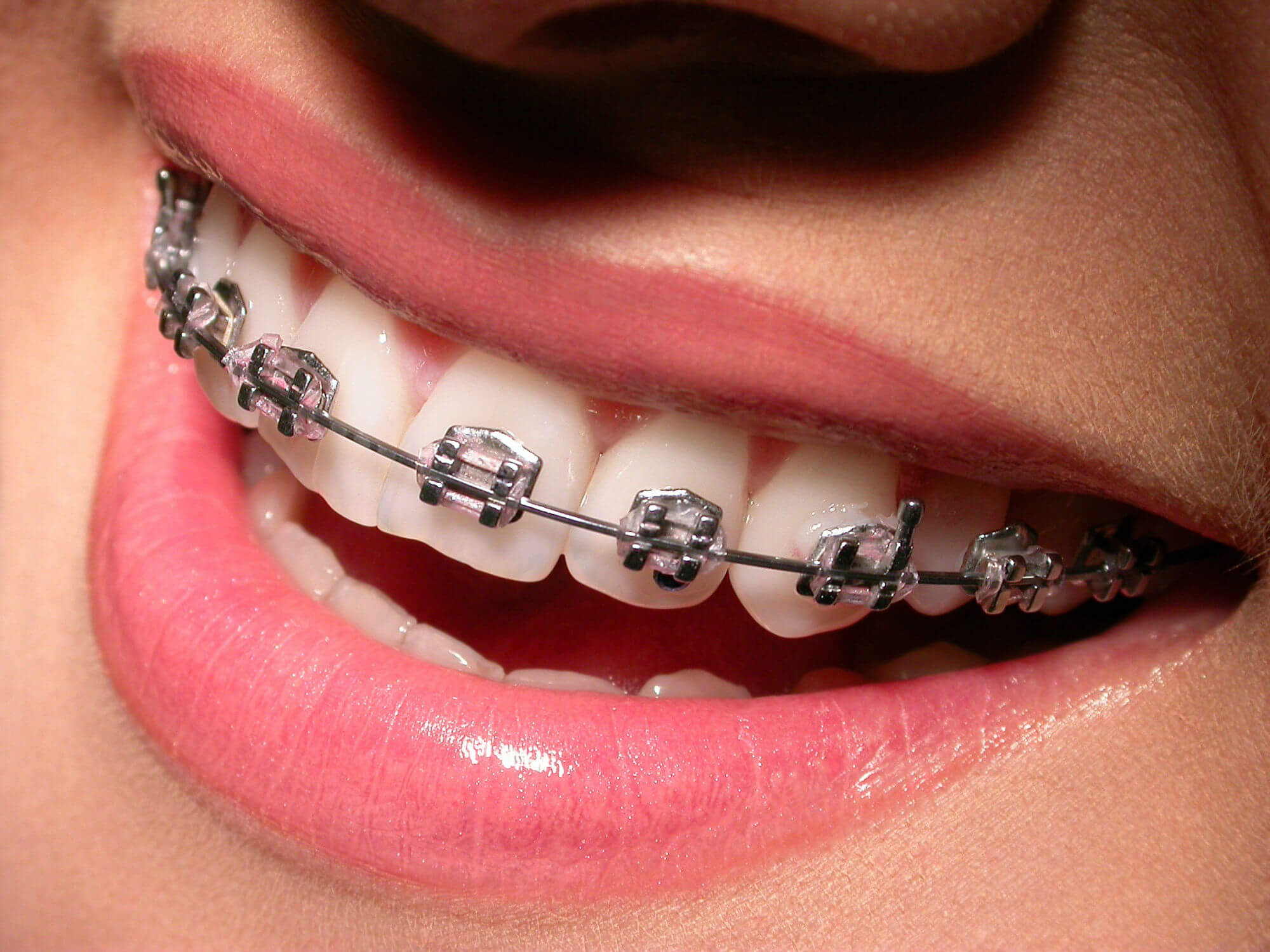
Orthodontics is a specialized branch of dentistry focused on the diagnosis, prevention, and correction of malpositioned teeth and jaws. It deals with the alignment of teeth, correction of bite issues (malocclusion), and guidance of facial development (particularly during growth phases).
What Is Orthodontics For? Purpose and Explanation 1. Straightening Teeth - Corrects crooked, rotated, or misaligned teeth to improve appearance and function. 2. Correcting Bite Issues - Fixes malocclusion (bad bite) like overbite, underbite, crossbite, or open bite. 3. Improving Jaw Alignment - Guides jaw growth in children and corrects skeletal problems in adults (with or without surgery). 4. Preventing Dental Problems - Misaligned teeth are harder to clean, which can lead to cavities, gum disease, or tooth loss. 5. Enhancing Facial Aesthetics - Improves the overall shape and harmony of the face, especially in growing children. 6. Speech and Chewing Correction - Proper alignment supports better pronunciation and efficient chewing. 7. Creating Space for Other Treatments - Prepares teeth positions for implants, bridges, or crowns.
Who Needs Orthodontics? Children with early signs of jaw or tooth development problems Teens with crowding, spacing, or bite issues Adults with relapsed alignment or new bite issues Patients preparing for oral surgery, prosthetics, or restorative treatments
Here's a main types of constructions used in orthodontics: 1. Fixed Appliances (Braces) These are attached to the teeth and not removable by the patient. a. Traditional Braces Metal brackets bonded to each tooth Archwires pass through brackets to apply force Ligatures (elastic or metal ties) hold wire in brackets Bands: Metal rings around molars Construction materials: Stainless steel, nickel-titanium (NiTi), beta-titanium
- b. Self-Ligating Braces Brackets have built-in clips instead of elastic ligatures Lower friction → potentially faster treatment Brands: Damon, In-Ovation c. Ceramic Braces Tooth-colored brackets for better aesthetics More brittle and slightly more expensive d. Lingual Braces Brackets placed behind the teeth (tongue side) Completely invisible from the front Requires custom lab fabrication using 3D scans (e.g., Incognito™, Harmony®) 2. Removable Appliances Removable by the patient; used in simpler cases or specific stages.a. Aligners (e.g., Invisalign) Series of clear plastic trays custom-made to move teeth Replaced every 1–2 weeks Ideal for mild to moderate cases 🧑💻 Constructed using 3D scanning, CAD software, and 3D printing
b. Retainers Used after active treatment to keep teeth in place. Hawley retainer: Acrylic base + metal wire across front teeth Essix retainer: Clear plastic tray (similar to aligner) Fixed retainer: Wire bonded behind front teeth
- c. Functional Appliances
Used mainly in growing children to modify jaw growth.
Twin Block: Two interlocking plates reposition lower jaw
Herbst appliance: Fixed metal rods hold lower jaw forward
Bionator, Frankel, Activator: Guide jaw and soft tissue growth
3. Auxiliaries & Force-Generating Devices
Used with fixed or removable systems to apply additional forces.
Elastics (rubber bands): Used to correct bite between upper/lower teeth
Coil springs: Open or close space
Power chains: Elastic chains to close gaps
Facebows & headgear: Extraoral appliances to restrict or direct growth
TADs (Temporary Anchorage Devices): Mini screws placed in bone to anchor certain tooth movements
4. Orthopedic Appliances
Target jaw bones rather than just teeth.
a. Palatal Expanders
Expand the upper jaw (maxilla) by separating the midpalatal suture
Often used in kids before puberty
Types:
Hyrax (screw-activated)
Quad Helix
Haas appliance
b. Reverse-Pull Headgear (Facemask)
Used for Class III (underbite) correction
Pulls upper jaw forward in growing children
c. Chin Cup
Controls excessive lower jaw growth in skeletal Class III patients Digital & 3D Constructions Modern orthodontics often uses digital modeling and printing: 3D intraoral scanners replace physical molds CAD/CAM systems design custom braces or aligners 3D-printed brackets, indirect bonding trays, and custom wires (e.g., SureSmile)